Innovation in a growing application
Vanadium is the main component (both cathode and anode) of the VRFB and VanadiumCorp has the security of supply in strategic mineral resources and 100% owned proprietary green and efficient recovery technology. Through strategic alliances, VanadiumCorp is participating in advancements pertaining to VRFB architecture and electrolyte chemistries. This strategy is aimed at facilitating the commercialization of proven VRFB technology, which is the fastest-growing application for vanadium today.

Filling a VRFB System with Electrolyte

VRFB Commissioning in the EU

Remote Battery Management & Electronics
High-Density Electrolyte & VRFB R&D
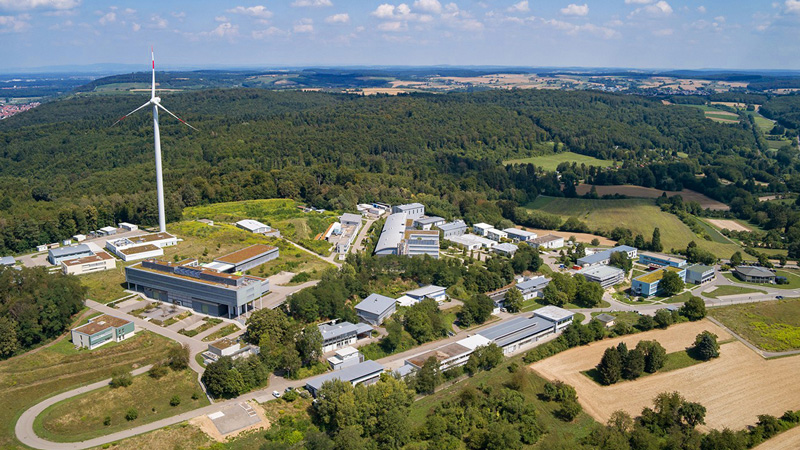

Renewable Energy Development
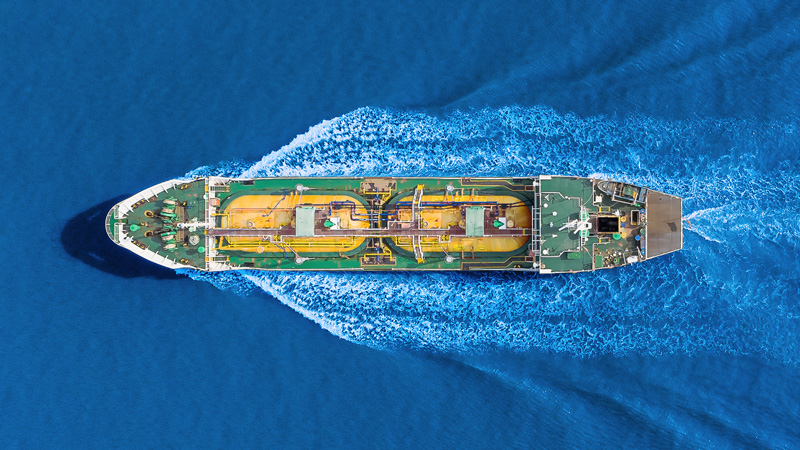

Zero-Emission Marine Vessel Development
Engineering & Development Network

Conoship International is an ambitious and innovative ship design and engineering office. Founded in 1952 as the central design office for a group of Northern Dutch shipyards, Conoship International developed a strikingly wide range of ships, from general cargo vessels, tankers, dredgers, to ferries and offshore vessels. Over 2,000 ships were built based on our designs, operating all around the world. We are passionate ship designers supporting our clients in realizing their vision during all phases of the shipbuilding process.

The Vega-Reederei GmbH & Co. KG can rely on the long-standing expertise of Vega-Reederei Friedrich Dauber GmbH & Co. KG can fall back on. The shipping company was founded in 1919 as a GmbH in Vienna and entered in the commercial register. In 1922 a branch office was opened in Hamburg to secure a business presence at the economically up-and-coming port.
Text for other or empty cell

Partnership with Fraunhofer ICT which is an integral part of the Karlsruhe International Sustainability Center (KISC) in Germany.

VanadiumCorp is Partnered with The German-Australian Alliance for Electrochemical Technologies for Storage of Renewable Energy. Learn More….

VanadiumCorp partnership & collaboration with UNSW’s world class researchers & access to cutting edge facilities
VanadiumCorp is partnered with Delectrik Systems and focused on sustainable and affordable VRFB Innovation

Israel Chemical Ltd. “ICL” is developing opportunities of the new bromine based technology for energy storage

VanadiumCorp is a research partner of the National Research Council (NRC CNRC), which is Canada’s largest federal research and development organization.
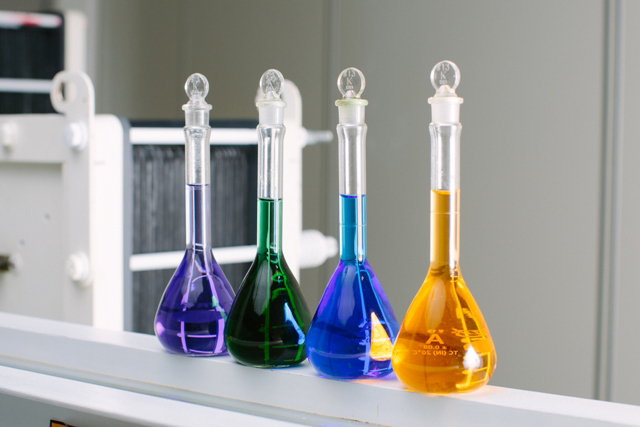

Key Areas of Innovation
- Energy density – Increasing energy density for VRFBs would increase demand for vanadium
- Power density – Increasing the power density will also result in increased uptake of vanadium in VRFBs
- Cost Reduction – Green & efficient recovery of vanadium & rental of the vanadium electrolyte could dramatically reduce the cost of VRFBs
- Performance – Higher efficiencies achieved through advanced and critical materials
- Sustainability (1st level) – Vanadium produced using 100% wholly-owned green process technology
- Sustainability (2nd level) – Vanadium electrolyte has unlimited use potential in VRFBs
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery “VRFB” 101
(Click Image to Open Slideshow)
The Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
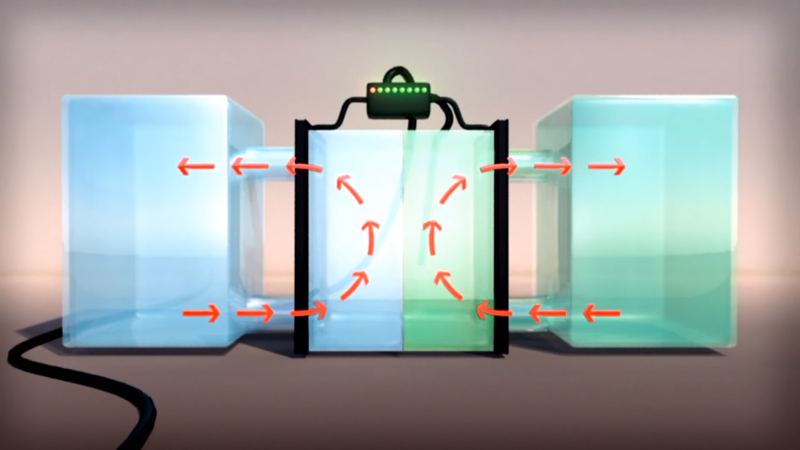
The VRFB is a type of rechargeable flow battery where rechargeability is provided by vanadium electrolyte (VE) dissolved in solution. The two tanks of Vanadium, one side containing V2+ and V3+ ions, the other side containing V4+ and V5+ ions, are separated by a thin proton exchange membrane. VRFBs consists of two tanks of vanadium electrolyte that flow adjacent to each other past a membrane and generate a charge by moving electrons back and forth during charging and discharging. This battery offers unlimited energy capacity simply by using larger electrolyte storage tanks. It can be left completely charged for long periods without losing capacity and maintenance is much simpler than other batteries. Pumps on both sides circulate the electrolyte.
The electron differential between the two cells generates electric power. Most batteries use two chemicals that change valence (or charge or redox state) and cross-contaminate and thus degrade over time. VRFBs utilize multiple valence states of vanadium as a single element to store and release charge. The VRFB has no cross-contamination like most batteries. The electrolyte in the catholyte and the anolyte consists of 100% vanadium ions. The ion-sensitive membrane separating both sides of the electrolyte tank allows only protons to pass. VRFBs are containerized, long duration, non-flammable, compact, reusable over infinite cycles, and last more than 20 years.
What are the advantages of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries?
- VRFBs have a lifespan of 20+ years
- VRFBs offer immediate energy release
- VRFBs are suitable for grid connection or off-grid settings – ideal for renewable energy
- VRFBs can discharge 100%, without any damage to the battery
- VRFBs are non-flammable
- They ensure power and energy can be scaled independently
- Vanadium electrolyte can be re-used and does not need to be disposed of
- The batteries can be cycled more than once per day
- They use only one element in electrolyte – V2O5
- VRFB energy storage guarantees uninterrupted power supply
How does a Vanadium Redox Flow battery (VRFB) work?
- A flow battery is charged and discharged by a reversible reduction-oxidation reaction between the two liquid vanadium electrolytes of the battery
- Unlike conventional batteries, electrolytes are stored in separated storage tanks, not in the power cell of the battery
- During operation, these electrolytes are pumped through a stack of power cells, in which an electrochemical reaction takes place and electricity is produced
(Click Image to Open Video)